We won’t dwell too much on what the actual tariffs are today, as they could be outdated within a few hours.
However, we will examine the effects.
Trump’s Tariff Objectives
- Boost US manufacturing by penalising offshore production.
- Reduce the trade deficit.
- Leverage trade policy for broader political objectives (e.g. immigration, national security).
- Apply strategic pressure.
- Fund tax cuts using tariff revenue.
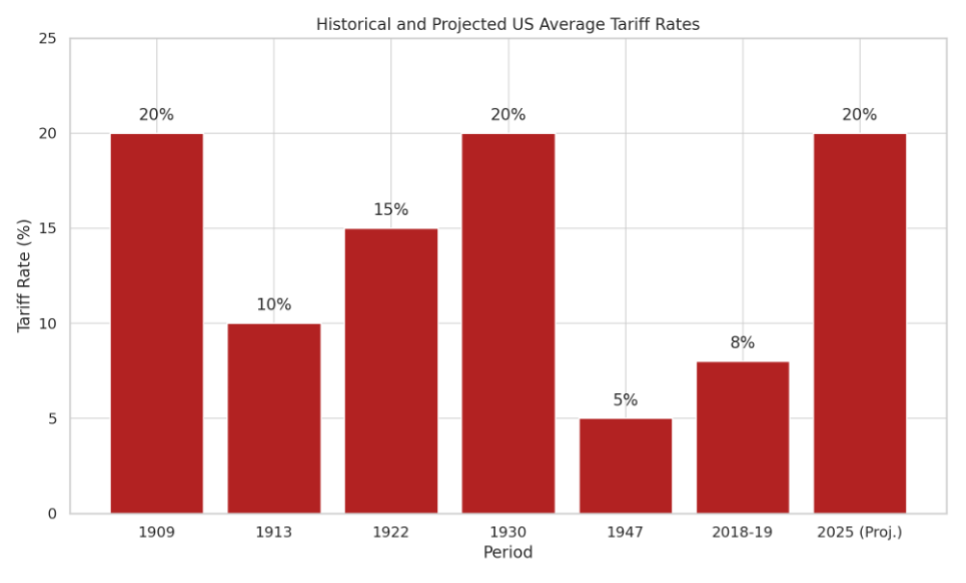
Source: Trading Economics
Tariffs have a two-fold effect:
- They make the cost of goods more expensive in the US in an attempt to reduce the demand for those goods by increasing the price people pay.
Consumers will only demand less of the imported goods if there is a local alternative; otherwise, they may still buy the imported product, albeit in smaller quantities.
And remember, building & commissioning (or recommissioning or refurbishing) manufacturing plants & industrial-sized infrastructure projects have long lead times. - Therefore, there will be less demand for the product or good from the country exporting it.
As an aside, could Trump’s ‘endgame’ be the forgiveness of US debt?
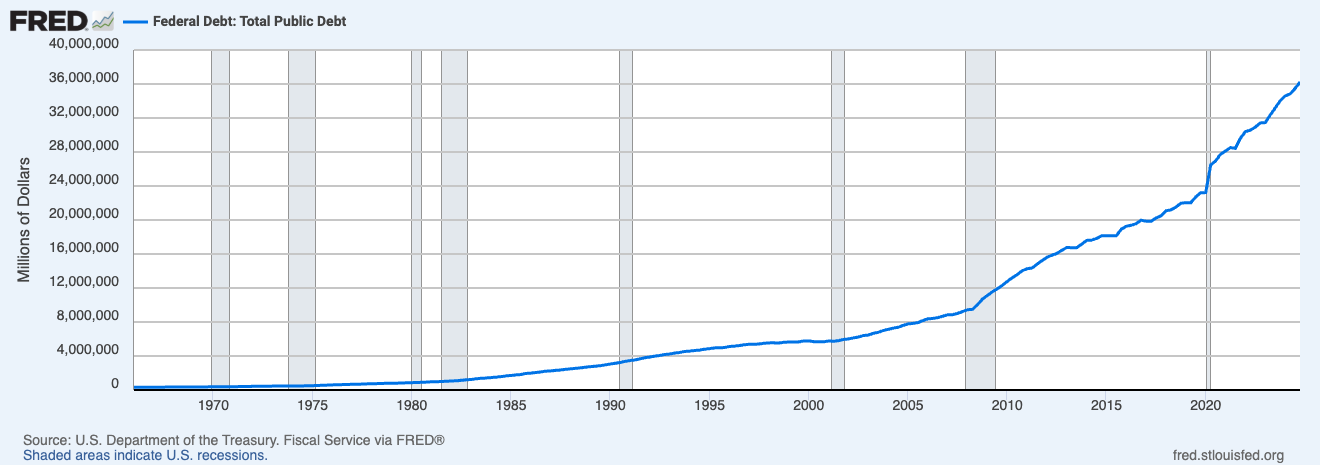
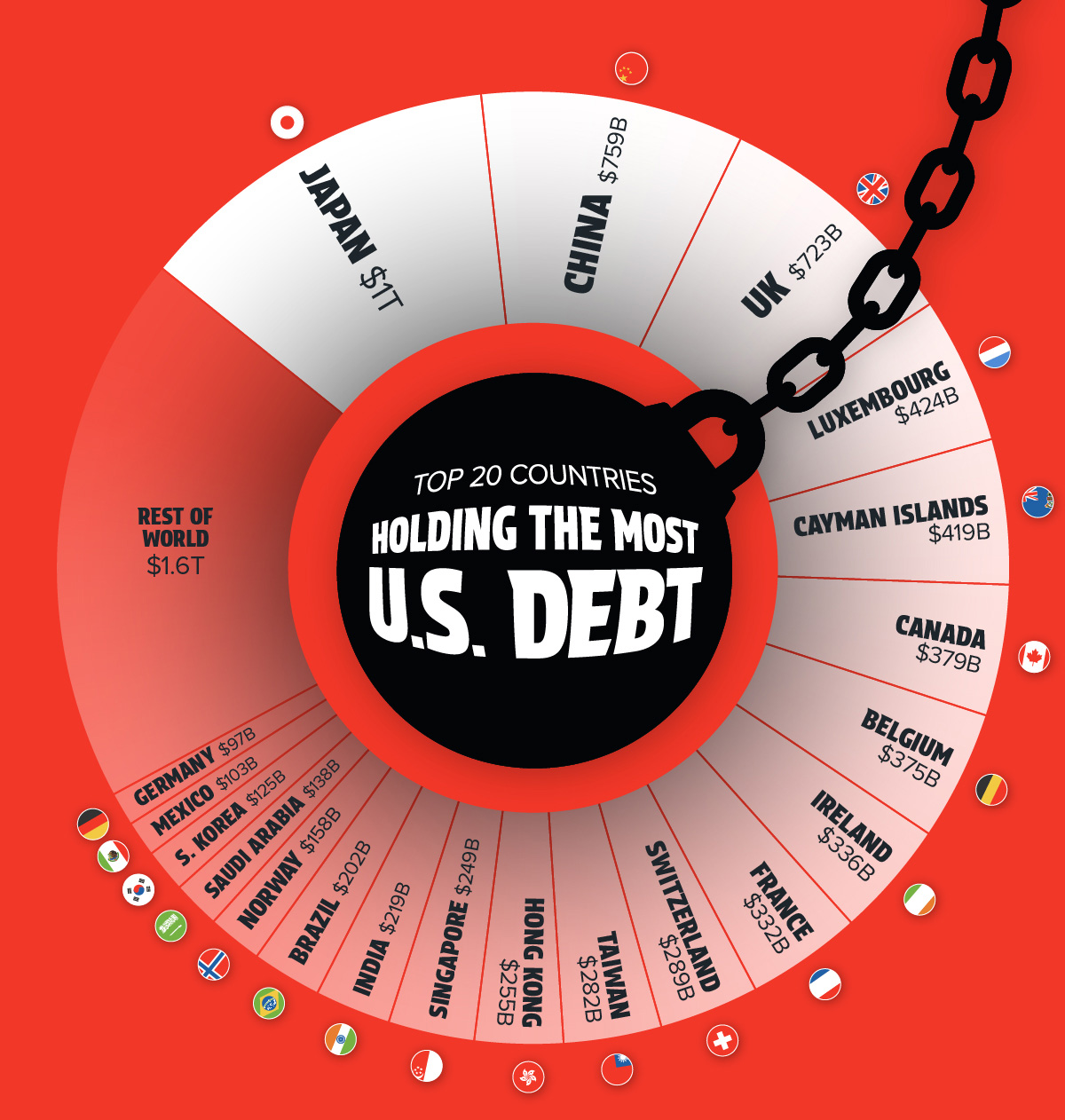
Source: Visual Capitalist
Funding tax cuts & markets
It remains unclear how or when Trump will renew the tax cuts passed in 2017, let alone the additional provisions.
It appears that the tariffs will take effect first, hence the market anxiety.
To be clear, the president does have a point when it comes to how Wall Street operates.
He says that he’s trying to make America great again, so the stock market’s daily movements are not his primary concern:
“What I have to do is build a strong country. You can’t really watch the stock market… If you look at China, they have a hundred-year perspective. We have a quarter. We go by quarters & you can’t go by that. You have to do what’s right. What we’re doing is, we’re building a tremendous foundation for the future.”
Recent Tariff Announcements
As we said at the outset, we won’t dwell too much on what the actual tariffs are right now, as they are ‘evolving’.
Despite these moves, President Trump has signalled a willingness to use tariffs as a negotiating tool, delaying or modifying them as needed.
How will tariffs impact the US economy?
- Estimates suggest that these new tariff increases could raise consumer prices by up to 2% (as 10% of US consumption is imported goods) & lower economic growth by 0.5 to 1%.
- The overall hit to US economic growth increases the chance of a recession, although it’s not inevitable – avoiding one may depend on the speed with which either Trump &/or the Fed respond to deteriorating economic conditions.
But economics is rarely that straightforward, is it?
Impact on Australia
- Direct exports to the US account for just 4% of Australia’s total exports.
- The main risk is slower Chinese growth, as China is our largest trading partner.
- Agriculture, mining, transport services, and pharmaceuticals are the most vulnerable sectors.
While the tariffs might negatively affect our exports, these markets will still have access to global trade. - Tariffs pose a greater threat to growth than inflation, supporting the RBA’s rate cut expectations.
Impact on other nations
- Canada & Mexico may face recessions. China’s GDP could fall by 0.5%, prompting policy stimulus.
- Inflation effects are likely to be mild unless prolonged, such as a one-off GST hike.
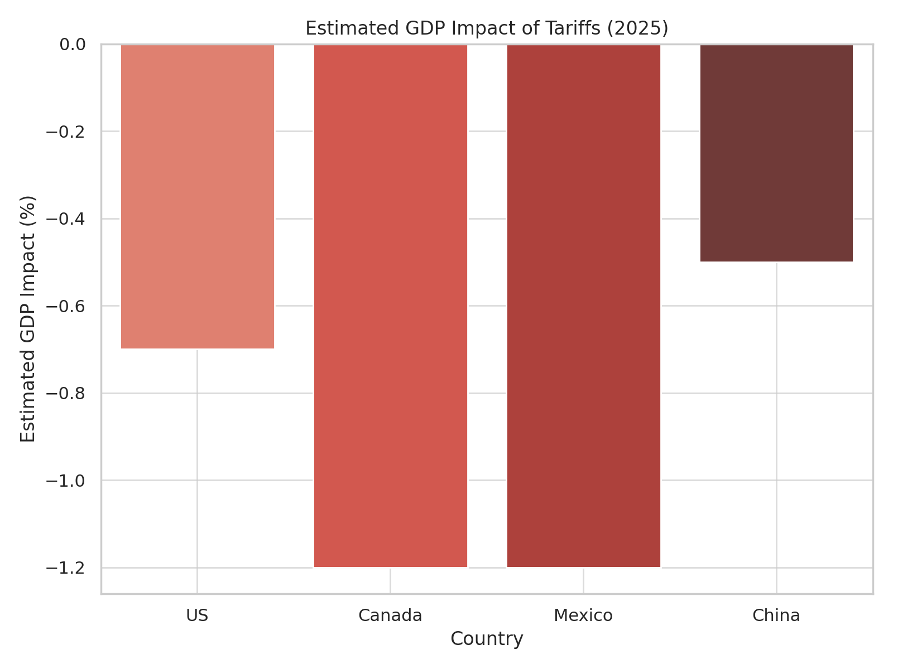
Source: Trading Economics
Market Impacts
- Equities are expected to be volatile, particularly outside the US.
- Emerging markets & Europe may outperform the US due to stimulus.
- US small-cap stocks are expected to be less affected than large-cap multinationals.
- The US dollar is expected to strengthen.
- Gold demand has risen as a safe haven.
Conclusion
While the rhetoric surrounding tariffs is aggressive, Trump’s pattern of “escalate then negotiate” means that some of the proposed tariffs may not be implemented.
Nevertheless, the uncertainty created is enough to disrupt markets, slow investment & impact economies, including Australia.
The best response for investors is to stay focused on long-term strategy & brace for volatility.
Further reading: Tariffs 101 What are they & how do they work/




